
ground state of electrons, the periodic trends such as ionization energy, and using valence electrons when drawing Lewis Dot Structures. With electron configurations we relate together Slater's rules and the Madelung rules when constructing our orbital diagrams.įrom what we've learned we can make connections with the quantum numbers, the bohr diagram when discussing the excited state vs. The electronic configuration of each element is decided by the Aufbau principle which states that the electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels. Remember that a neutral element is not allowed to possess a d 4 or d 9 orbital and so an electron from the s-orbital is promoted to the d-orbital.Įlectron Configuration Exception of CopperĪs stated previously, the electron configurations of the elements are essential in understanding the correlations between chemical and physical properties. Gray in Chemical Structure and bonding, Benjamin.
When an element is in its neutral form its electron configuration cannot possess a d 4 or d 9 orbital because of energetic reasons.įor example, Copper (Cu) has an atomic number of 29 and so possesses 29 electrons.įollowing the steps we have done we would obtain the following electron configuration for Copper: Literature sources Atomic, Molecular, & Optical Physics Handbook, Ed. Some elements will break the order of electrons and orbitals. Substituting in the is equivalent to writing 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 because both describe how 10 electrons are organized into orbitals. For example, the noble gas before we reach aluminum is neon. The condensed electron configuration begins at the noble gas just before we reach our specific element.
PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY WITH ELECTRON CONFIGURATION FULL
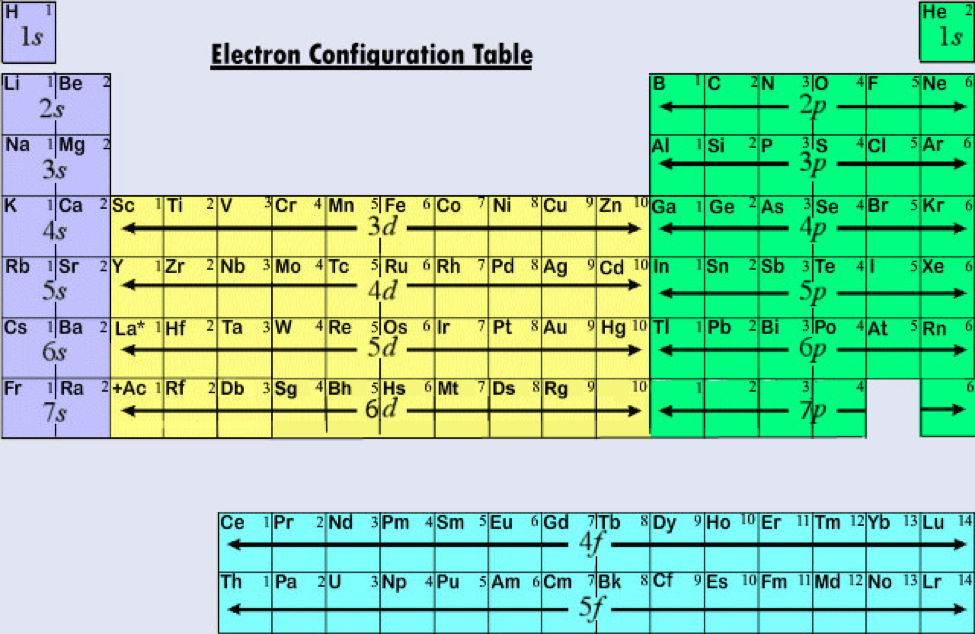
The full or longhand electron configuration involves going from the 1s orbital and to the last orbital of a specific element. If you wished to include the orbital diagram for the electron configuration for aluminum you would write the following:įull vs. Now we simply count to aluminum while filling in our various orbitals.Īl ( 13 Electrons) 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1 Looking at the periodic table we find that aluminum is in Group 3A and with an atomic number of 13 has 13 electrons total. This follows the aufbau principle, which in german means, “to build up”. In discussing the chemical properties of an element, we often focus on electrons in the outermost occupied energy level. STEP 2: Starting at the 1s orbital write the orbitals and the number of electrons involved with aluminum. STEP 1: Locate the element on the periodic table. Using this redesigned Periodic Table is an easy way to determine the electron configurations of all elements.įor example, what is the ground state electron configuration of Aluminum? Each atomic sub-level has a set number of atomic or electron orbitals with each being able to hold up to 2 electrons. The main atomic sub-levels or subshells are s, p, d and f. From this distribution of electrons we can relate the chemical and physical properties of different elements.īefore you begin the electron configuration of an element it is important to remember the basic principles of quantum mechanics. Periodic Trend: Successive Ionization EnergiesĪn element’s electron configuration represents the location of its electrons within various shells and orbitals.

Click on 'Element Atomic Number', 'Element Symbol', 'Element Name' and 'Element Electron Configuration' headers to sort.The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers This Electron Configuration table gives the Electron Configuration of all the elements of periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
